Yes, multimodal models can significantly contribute to personalized medicine by integrating diverse data sources to tailor medical treatments to individual patients. Here’s how:
1. Integrating Multiple Data Sources
Multimodal models can process various types of data, including medical images, electronic health records (EHRs), genetic information, and even patient-reported outcomes. By combining these data sources, they provide a more comprehensive view of a patient’s health, enabling more personalized treatment plans.
2. Predicting Treatment Responses
Stanford researchers have developed a multimodal AI model called MUSK that combines clinical notes and images to predict patient outcomes and responses to specific treatments. This model can help determine the best course of action for individual patients, especially in cancer care.
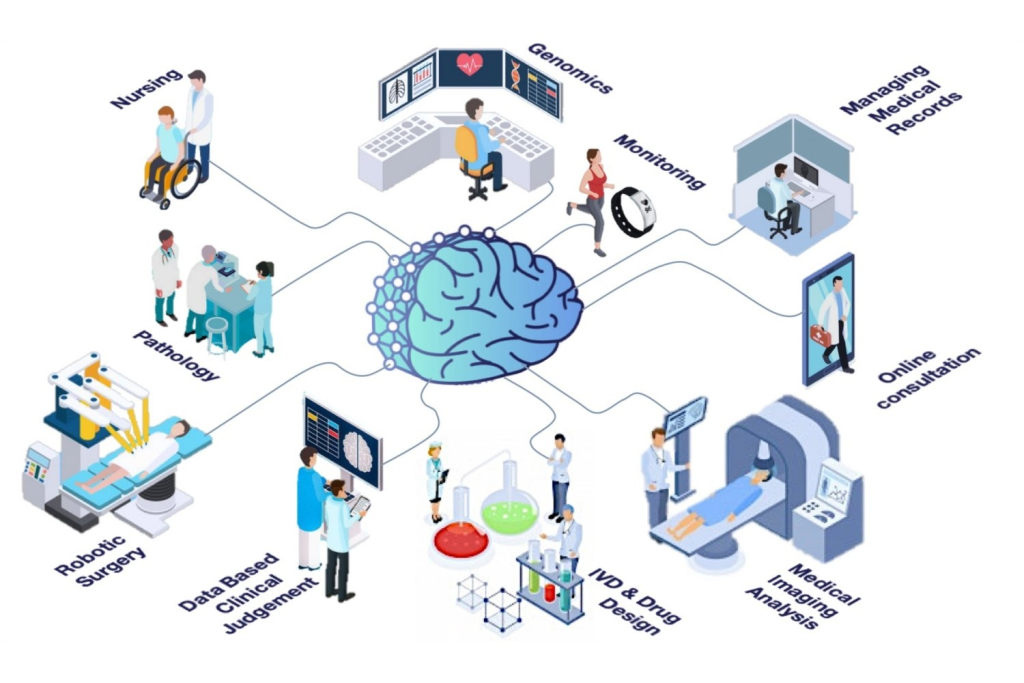
3. Enhancing Drug Development
Multimodal AI can integrate research publications, clinical results, and molecular structures to identify new uses for existing drugs. This approach can accelerate the development of personalized treatments by leveraging existing data and reducing the need for extensive new trials.
4. Improving Diagnostic Accuracy
By analyzing multimodal data, AI models can detect diseases earlier and more accurately. For example, integrating genetic data with clinical records can help identify patients who are at higher risk for certain conditions, allowing for more targeted interventions.
5. Facilitating Real-Time Monitoring
Multimodal models can also be used in real-time monitoring of patients. For instance, the VENTASTEP study by Bayer Vital GmbH integrated data from smart devices and digital tools to monitor patients’ responses to treatments. This real-time data collection and analysis can help adjust treatments as needed, ensuring they remain personalized and effective.
6. Addressing Ethical and Social Implications
As multimodal models become more prevalent in personalized medicine, ethical considerations such as data privacy and equitable access to advanced treatments will need to be addressed. Ensuring that all patients benefit from these advancements is crucial for the broader adoption of personalized medicine.
Conclusion
Multimodal models hold great promise for advancing personalized medicine by leveraging diverse data sources to create more accurate, effective, and patient-specific treatments. As these models continue to evolve, they will play an increasingly important role in transforming healthcare.