Multimodal models, such as those developed by DeepSeek, can significantly enhance disease diagnosis in biomedicine by integrating diverse types of data, including medical images, clinical text, and other relevant information. Here are several key ways in which multimodal models improve disease diagnosis:
1. Enhanced Accuracy through Data Integration
Multimodal models can process and integrate data from multiple sources, such as medical images (e.g., X-rays, CT scans, MRIs) and clinical text (e.g., electronic health records, radiology reports). By combining these different data modalities, the models can provide a more comprehensive understanding of a patient’s condition, leading to more accurate diagnoses. For example, DeepSeek’s models have demonstrated an 87.3% accuracy rate in medical image diagnosis tests, which is 15 percentage points higher than single-modality models.
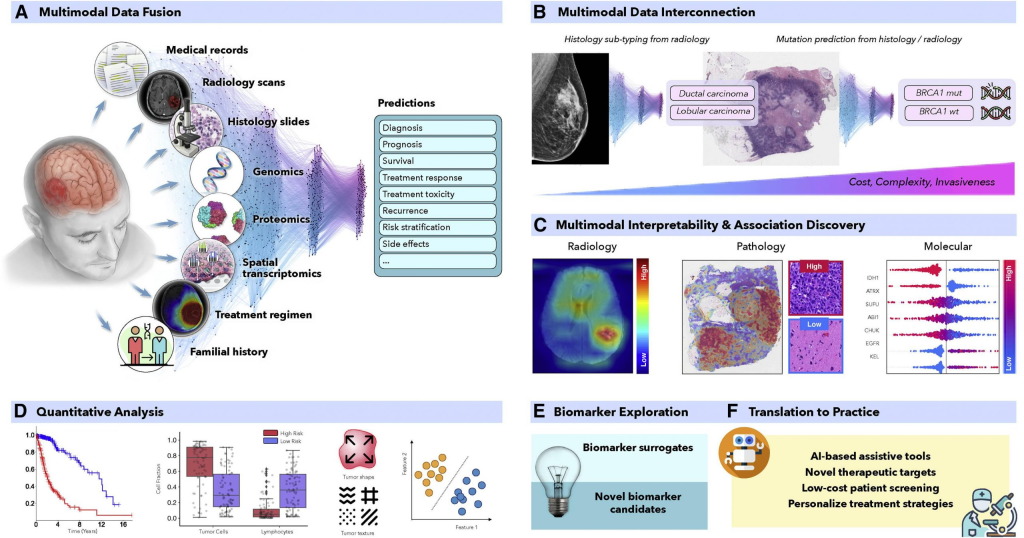
2. Improved Detection of Rare and Novel Diseases
One of the significant challenges in diagnosing rare and novel diseases is the lack of sufficient labeled training data. Multimodal models can leverage the available data more effectively by integrating various types of information. For instance, DeepSeek’s models have shown the ability to diagnose diseases that were not included in the training dataset, such as COVID-19, by recognizing subtle but important radiological differences. This capability is crucial during pandemics or when dealing with emerging diseases.
3. Cross-Modality Translation and Generation
Multimodal models can translate and generate data across different modalities. For example, they can convert CT scans to MRI images or generate synthetic medical images for training purposes. This ability not only helps in creating more diverse training datasets but also allows for better comparison and analysis of different imaging modalities, improving diagnostic accuracy.
4. Automated Report Generation
Generating medical reports from medical images is a time-consuming and error-prone task for clinicians. Multimodal models can automatically generate initial draft reports based on the analysis of medical images, which clinicians can then review and modify. This automation reduces the workload on medical professionals and decreases the likelihood of human error, thereby improving the overall quality of diagnosis.
5. Handling Multilingual and Multidomain Data
In a global healthcare setting, dealing with medical data in multiple languages and from different imaging domains is essential. Multimodal models can handle such diverse data, making them more versatile and applicable in different regions and healthcare systems. For example, DeepSeek’s models can align different domains across modalities and languages, enabling more accurate diagnosis even in zero-shot learning scenarios.
6. Reduced Reliance on Labeled Data
Traditional deep learning methods often require large volumes of labeled data, which can be expensive and time-consuming to obtain. Multimodal models, such as those developed by DeepSeek, can reduce this reliance by leveraging unsupervised and semi-supervised learning techniques. This makes the models more practical for real-world applications, especially in resource-limited settings.
7. Advanced Abnormality Detection and Lesion Segmentation
Multimodal models excel in detecting abnormal regions and segmenting lesions in medical images. For example, models like CXRBase and CT-CLIP have demonstrated robust performance in identifying abnormalities in chest radiographs and CT scans, respectively. These models can help in early detection and accurate assessment of diseases, leading to better treatment outcomes.
Conclusion
The integration of multimodal models into biomedicine represents a significant advancement in disease diagnosis. By leveraging diverse data sources and advanced AI techniques, these models can provide more accurate, efficient, and comprehensive diagnostic insights. DeepSeek’s ongoing research and development in this area are poised to further enhance the capabilities of multimodal models, ultimately leading to better patient care and outcomes.