The world of battery technology is on the brink of a significant transformation, driven by the rapid advancements in solid-state batteries. Companies like CATL, Toyota, and QuantumScape are at the forefront of this revolution, each contributing to the development and commercialization of next-generation batteries. This article delves into the current state and future prospects of half-solid state and full-solid state batteries, the challenges of thermal stability and mass production, and the impact of fast charging technologies on the electrical grid.
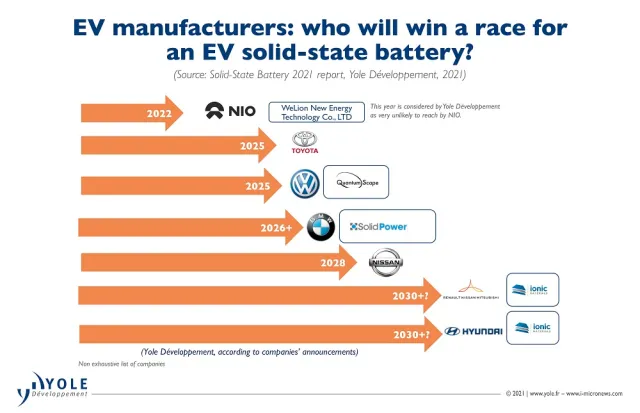
Half-Solid State Batteries: The Current State and Future Prospects CATL, a global leader in battery technology, has made substantial progress in the production of half-solid state batteries. These batteries are expected to see a significant reduction in cost to $100/kWh by 2025, while also achieving a range extension of up to 800 km. This breakthrough will not only make electric vehicles more affordable but also enhance their practicality for long-distance travel.
Full-Solid State Batteries: Research and Development While half-solid state batteries are making strides towards commercialization, full-solid state batteries remain in the research and development phase. Companies like Toyota and QuantumScape are actively working on this technology, which promises even greater improvements in safety, energy density, and charging speed. However, moving from the lab to mass production presents significant challenges that need to be overcome.

Thermal Stability and Mass Production Challenges One of the primary concerns with solid-state batteries is their thermal stability. Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries, solid-state batteries use solid electrolytes, which can be more prone to thermal issues under certain conditions. Ensuring that these batteries remain stable at high temperatures is crucial for their safety and reliability. Additionally, scaling up the production processes for solid-state batteries is a complex task. The unique materials and manufacturing techniques required pose significant hurdles in achieving mass production.
Fast Charging Technology Breakthroughs Fast charging technology has seen remarkable advancements in recent years. These breakthroughs have the potential to significantly reduce charging times, making electric vehicles more convenient for consumers. However, fast charging also comes with its own set of challenges, particularly in terms of battery life and performance. Repeated fast charging cycles can lead to degradation of the battery, reducing its overall lifespan.
Grid Load Challenges Posed by Fast Charging The widespread adoption of fast charging technologies poses significant challenges to the electrical grid. Fast charging stations require high levels of power, which can place a substantial load on the grid, especially during peak hours. This increased demand can lead to voltage fluctuations and potential power outages if not managed properly. To address these challenges, infrastructure improvements and smart grid technologies will be essential to ensure a stable and reliable power supply.
Conclusion The future of battery technology looks promising with the ongoing advancements in solid-state batteries and fast charging technologies. While there are still challenges to overcome, particularly in terms of thermal stability and mass production, the potential benefits are substantial. As companies like CATL, Toyota, and QuantumScape continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, we can expect to see significant improvements in the performance, safety, and affordability of electric vehicles in the coming years.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the main difference between half-solid state and full-solid state batteries?
- Half-solid state batteries still retain some liquid components, whereas full-solid state batteries use solid electrolytes throughout. This makes full-solid state batteries potentially safer and more energy-dense.
- How will the cost reduction of half-solid state batteries impact the electric vehicle market?
- A cost reduction to $100/kWh will make electric vehicles more competitive with traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, driving further adoption.
- What are the main challenges in scaling up solid-state battery production?
- The primary challenges include developing cost-effective manufacturing processes, ensuring the quality and consistency of solid electrolytes, and addressing thermal stability issues.
- Can fast charging damage solid-state batteries?
- While fast charging can lead to battery degradation over time, advancements in battery management systems and materials are helping to mitigate these effects.
- What infrastructure improvements are needed to support fast charging stations?
- Upgrades to the electrical grid, including higher capacity transformers and smart grid technologies, are necessary to manage the increased load.
- When can we expect full-solid state batteries to be commercially available?
- While timelines vary, most experts predict that full-solid state batteries will enter the market in the next 5-10 years, with ongoing research and development driving progress.